ISO 27001 is an international standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS), jointly developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
It provides a risk-based framework for managing confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets, helping organizations prevent security incidents and comply with legal and regulatory requirements.
Built on a risk management structure, ISO 27001 enables organizations to identify, assess, and manage information security risks while protecting their information assets from internal and external threats through a systematic approach.
Organizations implementing ISO 27001 can expect the following benefits:
Protection of Information Assets
● Ensures confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data
● Protects information assets from internal and external security threats
Compliance with Legal Requirements
● Supports compliance with data protection laws such as GDPR and local privacy regulations
● Reduces legal risks and the likelihood of financial penalties
Prevention of Cyberattacks and Security Incidents
● Shields the organization from ransomware, hacking, data breaches, and other cyber threats
● Enables swift response and recovery through established incident handling procedures
Business Continuity
● Minimizes operational disruptions caused by security incidents
● Supports business continuity planning (BCP) and disaster recovery (DR) frameworks
Enhanced Customer Trust and Corporate Image
● Strengthens trust in the organization's information security measures
● Improves credibility with clients, partners, and stakeholders
Increased Competitiveness and Global Market Access
● Enables international expansion by meeting global information security standards
● Provides a competitive edge in bids and tenders through recognized certification
This standard is applicable to organizations of all sizes and industries, and is especially valuable for:
● IT companies and software developers
● Financial institutions and insurance providers
● Hospitals and pharmaceutical companies
● Public institutions and educational organizations
● Manufacturers and distributors
● Cloud service providers and data centers
● Ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets
● Establishes a preventive and responsive system for cybersecurity incidents
● Supports compliance with legal and regulatory requirements
● Enhances organizational credibility and competitiveness
● Serves as a critical certification for accessing global markets
ISO 27001 operates based on the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle.
| Phase | Key Activities |
|---|---|
| Plan | ● Establish information security policies ● Plan for risk assessment and risk treatment measures |
| Do | ● Implement security controls ● Conduct security awareness training for employees |
| Check | ● Evaluate the performance of security management ● Perform internal audits and management reviews |
| Act | ● Address identified vulnerabilities ● Ensure continual improvement of the information security management system |
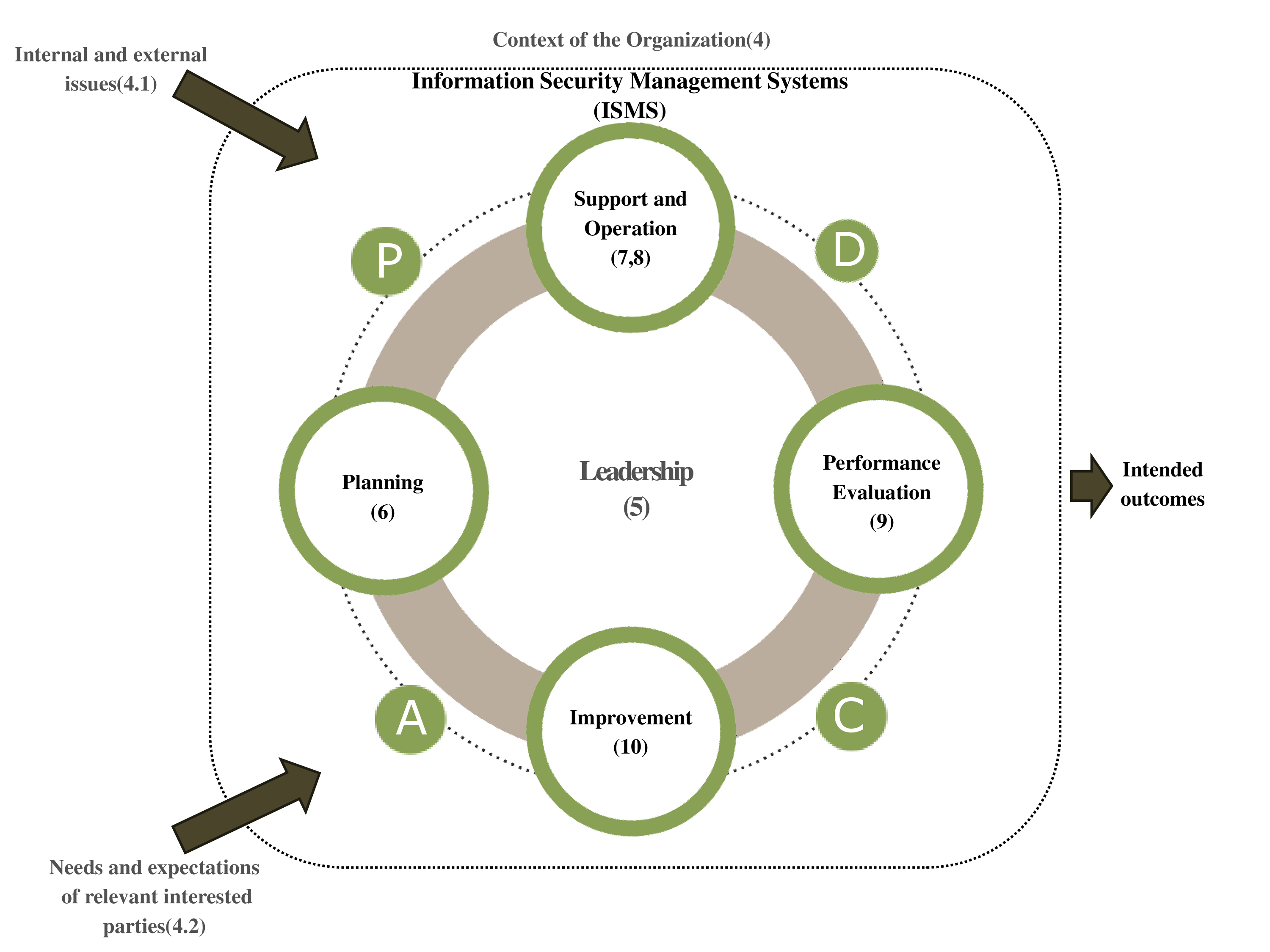
The success of an Information Security Management System (ISMS) depends on the leadership of top management and the active involvement of all levels within the organization. By leveraging a well-defined information security strategy, organizations can prevent cyber threats, ensure business continuity, and enhance their competitiveness.
Top management must integrate information security into business processes, strategic planning, and decision-making, treating it with equal importance as other key management components.
The complexity, level of documentation, and resource requirements of an ISMS vary depending on several factors, including the organization's size, operational methods, level of security risk, legal obligations, and the nature of its services and products.
An ISMS plays a critical role in continuously improving the protection of information assets and adapting to the evolving security landscape.
Contact Person
kgb@icrqa.com
lee2750@icrqa.com